Historical Baseline Study Ongoing Monitoring No Ground Installation
InSAR, meaning “Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar”, is a remote sensing technique that utilises satellite radar imagery to accurately measure millimetre scale ground displacements on the Earth’s surface.
Measure Millimetre Ground Movement from Space
Repeat satellite images acquired over the same area for a period of time are processed with complex algorithms to produce maps that highlight and quantify ground stability and movement to the nearest millimetre.
1000’s Measurement Points Historical Time-Series Cross-Sections
Archives containing years of radar imagery can be exploited to go back in time and reconstruct historical ground movement over an area and create baseline studies where historical ground stability needs to be quantified. Dozens of radar satellites acquire new imagery every few days for the entire globe, enabling continuous monitoring of ground movement for ongoing projects or ‘at-risk’ areas.
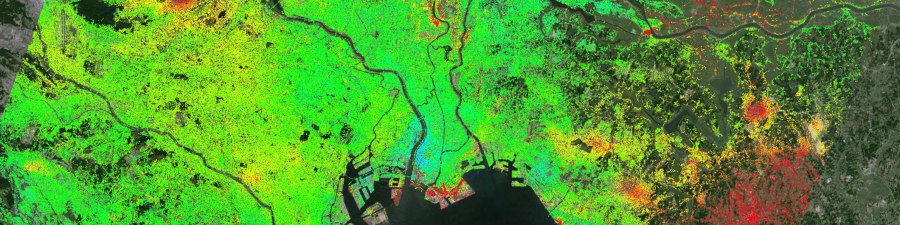
Example Dense InSAR Data Points over an Urban Environment: InSAR measurement points over a wide area, coving both a mixed urban and rural environment. Example shows the extremely dense dataset a single analysis can produce – millions of measurement points from one satellite frame, with no ground instrumentation required. Red measurement points indicate movement away from the satellite (typically subsidence), green indicates stability and blue is towards the satellite (typically uplift) [Img src TRE-Altamira]
Mapping with InSAR ensures
- Wide-area coverage
- No ground installation required
- Synoptic overview of ground movement
- Dense datasets – thousands of measurement points over survey area
- Rapid frequency baseline mapping
- Historical analyses – go back in time using existing image databases
- Maps are complimentary to existing ground-based instrumentation
Our Sectors & Applications Our Partners Contact Us